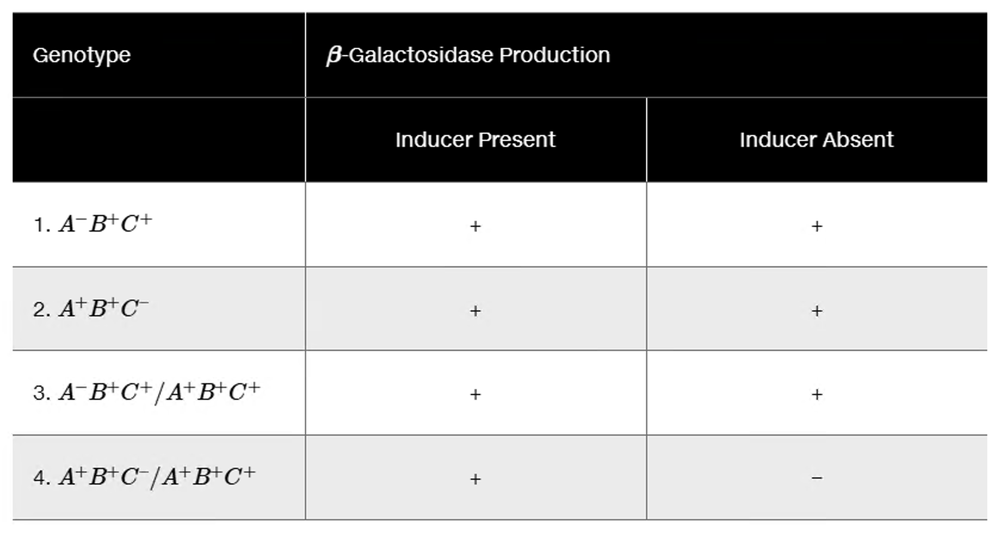
Suppose that base substitution mutations sufficient to eliminate the function of the operator regions listed below were to occur. For each case, describe how transcription or life cycle would be affected.
lacO mutation in E. coli
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

