Why do most cancers require the mutation of multiple genes?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
19. Cancer Genetics
Cancer Mutations
Problem C.9d
Textbook Question
Go to the website http://www.cancer.gov and select 'Cancer Types' on the top menu bar. Scroll down to 'Breast Cancer' and click. Select 'Cases & Prevention' from the options. Click 'More information' and select 'BRCA Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing'. Use the information on this page to answer the following questions. Are there measures a woman with a positive result can take to lessen her chances of developing cancer or to catch a cancer early in its development?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
This question is about understanding genetic risk factors and preventive measures related to BRCA mutations, which are linked to breast cancer risk.
First, recognize that BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes where certain mutations can significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
Next, explore the information on the specified website section about BRCA mutations, focusing on recommended strategies for women who test positive for these mutations.
Identify the preventive measures mentioned, which may include increased surveillance (such as more frequent mammograms or MRI scans), lifestyle changes, chemoprevention (using medications to reduce risk), and prophylactic surgeries (such as mastectomy or oophorectomy) to reduce cancer risk.
Finally, understand that early detection strategies aim to catch cancer at an early, more treatable stage, while preventive surgeries and medications aim to lower the overall risk of developing cancer.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
BRCA Gene Mutations and Cancer Risk
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes that produce proteins responsible for repairing DNA damage. Mutations in these genes can significantly increase a woman's risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers. Understanding these mutations helps assess individual cancer risk and guides decisions about prevention and screening.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cancer Mutations
Preventive Measures for High-Risk Individuals
Women with positive BRCA mutations can take preventive actions such as increased surveillance, chemoprevention, or risk-reducing surgeries like mastectomy or oophorectomy. These measures aim to lower the chance of cancer development or detect it early when treatment is more effective.
Recommended video:
Guided course
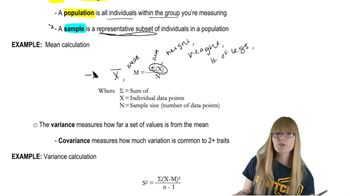
Mathematical Measurements
Early Detection and Screening Strategies
Early detection involves regular screening methods like mammograms, MRI, and clinical breast exams, especially for high-risk women. These strategies help identify cancer at an early stage, improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cell-cell interactions
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
362
views


