How many Barr bodies are found in a normal human female nucleus? In a normal male nucleus?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Sex Chromosome
Problem 11
Textbook Question
What is the basis for homology among chromosomes?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Homology among chromosomes is based on the similarity in their DNA sequences, which indicates a shared evolutionary origin.
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes (one from each parent) that have the same genes at the same loci, but they may have different alleles for those genes.
The structural basis for homology includes similar length, centromere position, and banding patterns when stained during karyotyping.
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up in a process called synapsis, facilitated by the synaptonemal complex, which ensures proper alignment and recombination.
Homology is critical for genetic recombination (crossing over) during meiosis, which increases genetic diversity by exchanging genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromosomal Homology
Chromosomal homology refers to the similarity between chromosomes that arise from shared ancestry. Homologous chromosomes have the same genes at the same loci, but may carry different alleles. This concept is crucial for understanding genetic variation and inheritance patterns, as homologous chromosomes pair during meiosis, facilitating genetic recombination.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Gene Structure and Function
Genes are segments of DNA that encode for proteins and determine traits. Understanding gene structure, including exons and introns, is essential for grasping how homologous chromosomes can carry variations of the same gene. This knowledge helps explain how genetic diversity arises through mutations and recombination during sexual reproduction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Meiosis and Genetic Recombination
Meiosis is the process of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes undergo recombination, where segments of DNA are exchanged, leading to genetic diversity. This process is fundamental to understanding how homologous chromosomes contribute to variation in offspring and the evolutionary significance of genetic diversity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
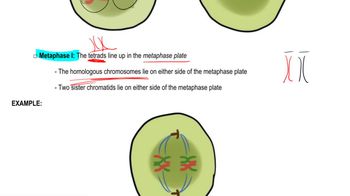
Meiosis Steps
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
474
views


