Ribosomal assembly occurs where in the cell?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
11. Translation
Ribosomal Structure
Problem 12a
Textbook Question
The diagram of a eukaryotic ribosome shown below contains several errors.
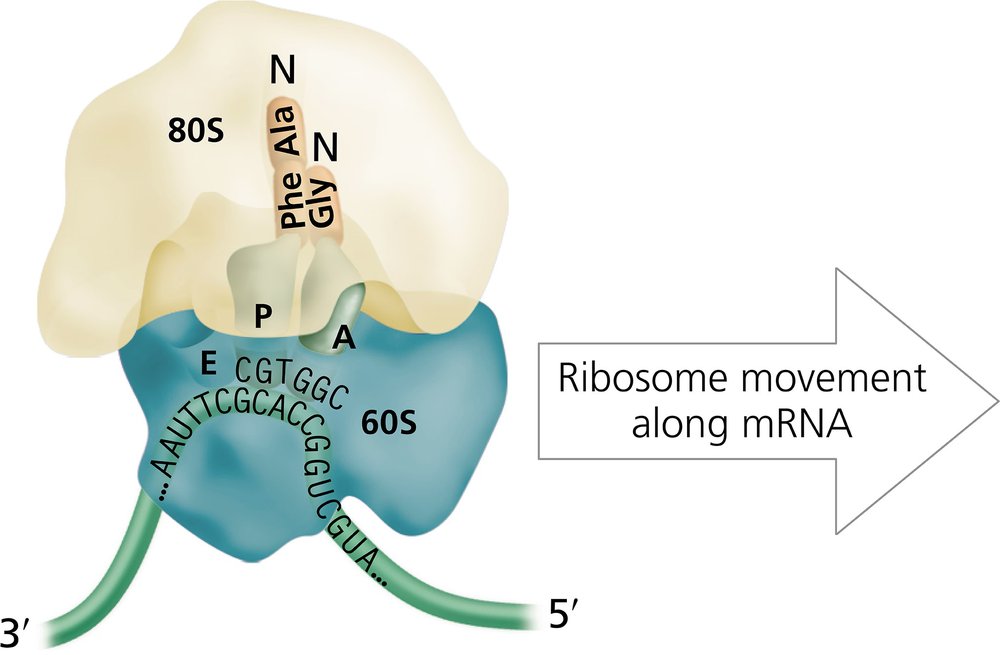
Examine the diagram carefully, and identify each error.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Carefully examine the diagram of the eukaryotic ribosome provided in the problem. Identify the key components of a eukaryotic ribosome, such as the large subunit (60S), small subunit (40S), mRNA, tRNA, and the A (aminoacyl), P (peptidyl), and E (exit) sites.
Compare the labels and structures in the diagram to the correct organization of a eukaryotic ribosome. Check if the subunits are labeled correctly (e.g., 60S and 40S for eukaryotes, not 50S and 30S, which are prokaryotic).
Verify the placement of the A, P, and E sites within the ribosome. Ensure that the A site is where the aminoacyl-tRNA enters, the P site is where the peptide bond forms, and the E site is where the tRNA exits.
Check the orientation of the mRNA strand in the diagram. Ensure that the mRNA is correctly positioned to be read in the 5' to 3' direction by the ribosome.
Identify any other structural or labeling errors, such as incorrect depiction of tRNA binding, peptide bond formation, or the ribosome's interaction with the mRNA and associated factors.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Eukaryotic Ribosome Structure
Eukaryotic ribosomes are complex molecular machines composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. They consist of two subunits: the large subunit (60S) and the small subunit (40S), which come together during protein synthesis. Understanding the structure is crucial for identifying errors in diagrams, as each component plays a specific role in translation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a fundamental component of ribosomes, providing structural support and catalyzing peptide bond formation during protein synthesis. In eukaryotes, rRNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA and is essential for the proper assembly and function of ribosomal subunits. Errors in the representation of rRNA can lead to misunderstandings about ribosome function.
Recommended video:
Translation Process
Translation is the process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins by decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences. This involves the sequential addition of amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain, guided by the mRNA template. Recognizing errors in a ribosome diagram requires an understanding of how the ribosome interacts with mRNA and transfer RNA (tRNA) during this critical biological process.
Recommended video:
Guided course

mRNA Processing
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice



