What evidence indicates that mutations in human DNA mismatch repair genes are related to certain forms of cancer?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
19. Cancer Genetics
Cancer Mutations
Problem 28a
Textbook Question
The table in this problem summarizes some of the data that have been collected on mutations in the BRCA1 tumor-suppressor gene in families with a high incidence of both early-onset breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
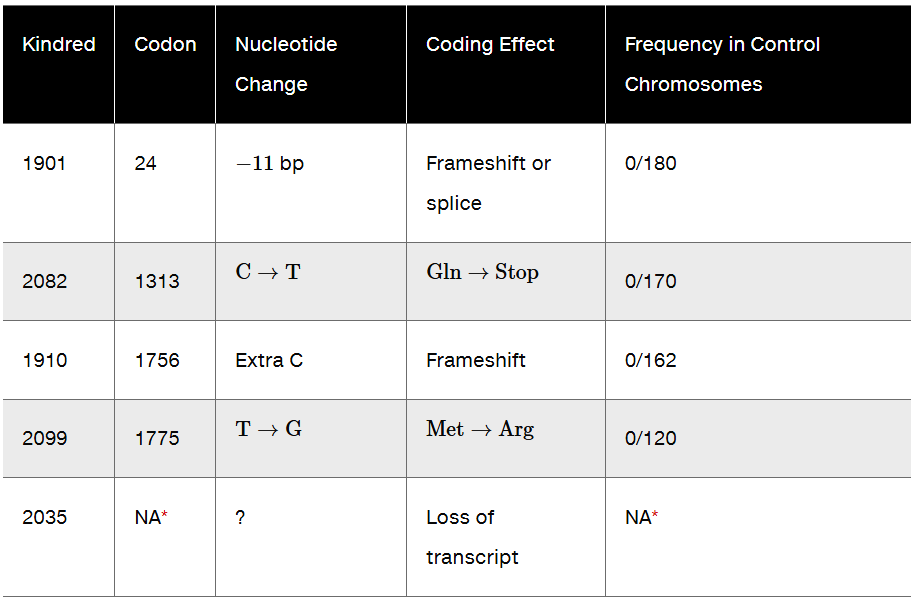
Note the coding effect of the mutation found in kindred group 2082. This results from a single base-pair substitution. Draw the normal double-stranded DNA sequence for this codon (with the 5' and 3' ends labeled), and show the sequence of events that generated this mutation, assuming that it resulted from an uncorrected mismatch event during DNA replication.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the normal codon sequence for kindred group 2082. The mutation involves a single base-pair substitution (C→T) at codon 1313, which changes the amino acid from glutamine (Gln) to a stop codon. Determine the normal DNA sequence for the codon encoding glutamine. Glutamine is encoded by the codons CAA or CAG in mRNA, which corresponds to the DNA sequence GTT or GTC on the template strand (5' to 3').
Step 2: Write the normal double-stranded DNA sequence for the codon. For example, if the codon is CAA in mRNA, the corresponding DNA sequence would be: Template strand (5' to 3'): GTT; Coding strand (3' to 5'): CAA. Label the 5' and 3' ends of both strands.
Step 3: Illustrate the mismatch event during DNA replication that leads to the mutation. During replication, a cytosine (C) on the template strand is incorrectly paired with adenine (A) instead of guanine (G). This mismatch occurs due to an error in base pairing.
Step 4: Show how the mismatch is uncorrected during subsequent replication cycles. If the mismatch is not repaired, the adenine (A) on the newly synthesized strand will pair with thymine (T) in the next round of replication, resulting in a permanent substitution of C→T in the DNA sequence.
Step 5: Write the mutated double-stranded DNA sequence. After the mutation, the template strand (5' to 3') will have GTT replaced by ATT, and the coding strand (3' to 5') will have CAA replaced by TAA. Label the 5' and 3' ends of both strands and note that TAA is a stop codon, leading to premature termination of translation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
BRCA1 Gene Function
The BRCA1 gene is a crucial tumor-suppressor gene that plays a significant role in maintaining genomic stability by repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Mutations in this gene can lead to a loss of function, increasing the risk of breast and ovarian cancers. Understanding its normal function helps in comprehending how specific mutations can disrupt cellular processes and contribute to cancer development.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Types of Mutations
Mutations can be classified into several types, including point mutations, insertions, deletions, and frameshifts. A point mutation involves a change in a single nucleotide, which can lead to a different amino acid being incorporated into a protein or a premature stop codon. Recognizing these types is essential for analyzing how specific genetic changes affect protein function and contribute to disease.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes
DNA Replication and Mismatch Repair
During DNA replication, errors can occur, leading to mismatches between base pairs. The mismatch repair system is responsible for correcting these errors; however, if a mismatch is not corrected, it can result in a permanent mutation. Understanding the process of DNA replication and the role of mismatch repair is vital for explaining how mutations arise and their potential consequences on gene function.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Repair Pathways
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
471
views


