Look closely at the consolidated Hfr map and the data used to build the map on page 261. Suppose a fifth Hfr strain had the F factor inserted exactly halfway between cysE and leuU and had an orientation that was the same as that of Hfr 1. List the order of gene transfer for the first six genes transferred by this Hfr and the number of minutes of conjugation at which each gene is expected to be seen.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacterial Conjugation
Problem 29a
Textbook Question
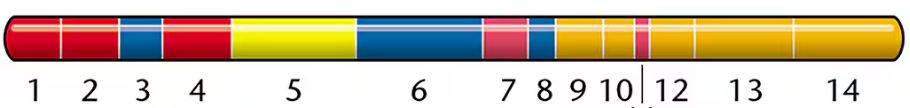
A study was conducted in an attempt to determine which functional regions of a particular conjugative transfer gene (tra1) are involved in the transfer of plasmid R27 in Salmonella enterica. The R27 plasmid is of significant clinical interest because it is capable of encoding multiple-antibiotic resistance to typhoid fever. To identify functional regions responsible for conjugal transfer, an analysis was conducted by Lawley et al. (2002). J. Bacteriol. 184:2173-2180 was conducted in which particular regions of the tra1 gene were mutated and tested for their impact on conjugation. Shown here is a map of the regions tested and believed to be involved in conjugative transfer of the plasmid. Similar coloring indicates related function. Numbers correspond to each functional region subjected to mutation analysis.
Accompanying the map is a table showing the effects of these mutations on R27 conjugation.
Effects of Mutations in Functional Regions of Transfer Region 1 (tra1) on R27 Conjugation
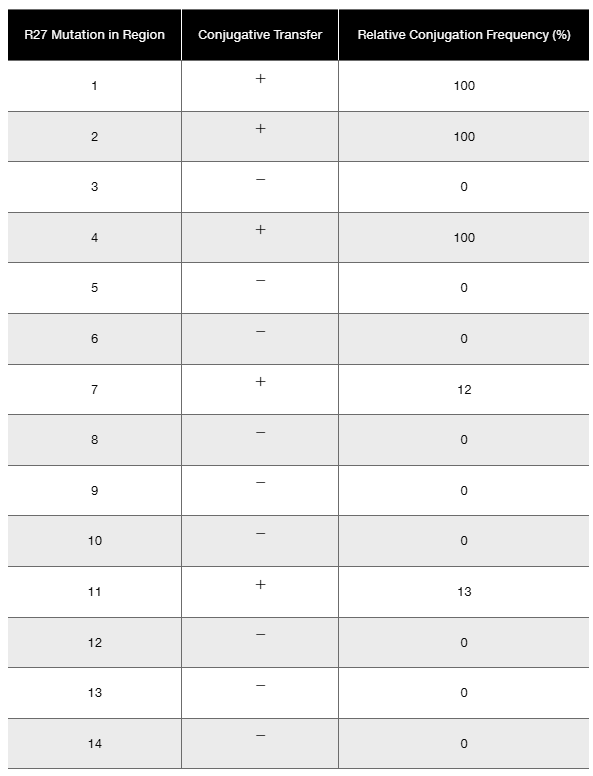
Given the data, do all functional regions appear to influence conjugative transfer?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the color-coded map of the tra1 gene, noting that it is divided into 14 functional regions, each numbered from 1 to 14 and grouped by color to indicate related functions.
Understand that mutations were introduced into each of these regions to assess their impact on the conjugative transfer of the R27 plasmid in Salmonella enterica.
Recognize that if a mutation in a particular region significantly reduces or abolishes conjugative transfer, that region is likely important for the process.
Compare the transfer rates or functional outcomes associated with mutations in each region to determine which regions affect conjugation and which do not.
Conclude that not all regions may influence conjugative transfer equally; some regions might show no effect when mutated, indicating they are not essential for the transfer function.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Conjugative Transfer and Plasmids
Conjugative transfer is a process where genetic material, typically plasmids, is transferred between bacteria through direct contact. Plasmids like R27 carry genes that can confer traits such as antibiotic resistance, making their transfer clinically significant. Understanding which gene regions control this transfer helps in combating the spread of resistance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

R Plasmid
Functional Regions of Genes and Mutation Analysis
Genes often contain multiple functional regions, each responsible for specific activities or interactions. Mutation analysis involves altering these regions to observe changes in function, helping identify which parts are essential. In this study, mutating different regions of the tra1 gene reveals their role in plasmid conjugation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Interpreting Color-Coded Genetic Maps
Color-coded maps visually group gene regions by related functions, aiding in understanding complex genetic structures. In the image, regions with similar colors share functional roles, and numbers indicate mutation sites tested. This helps correlate specific mutations with their impact on conjugative transfer efficiency.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Genetic Code
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
354
views


