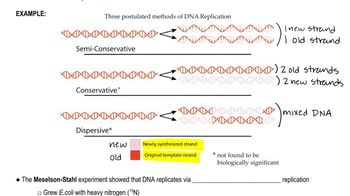
Answer the following questions concerning the accuracy of DNA polymerase during replication.
Identify two mechanisms that can correct the kind of abnormality resulting from the circumstances identified in part (c).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: