How do we know the age of the last common ancestor shared by two species?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
21. Population Genetics
Allelic Frequency Changes
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
How do we know how much genetic variation is in a population?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that genetic variation in a population refers to the differences in DNA sequences among individuals, which can be measured at the level of genes or entire genomes.
Recognize that to quantify genetic variation, scientists often collect samples from the population and analyze specific genetic markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), microsatellites, or allozymes.
Use molecular techniques like DNA sequencing or genotyping to identify the different alleles present at various loci within the sampled individuals.
Calculate measures of genetic diversity such as allele frequencies, heterozygosity (the proportion of individuals that are heterozygous at a locus), and nucleotide diversity, which provide numerical estimates of variation.
Interpret these measures in the context of the population's size, structure, and evolutionary forces to understand the extent and distribution of genetic variation.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation refers to the differences in DNA sequences among individuals within a population. It is the raw material for evolution and can be measured by examining differences in alleles, genotypes, or phenotypes. Understanding the extent of genetic variation helps in assessing a population's potential to adapt to environmental changes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genomic Variation
Molecular Markers and Genotyping
Molecular markers such as microsatellites, SNPs, and allozymes are tools used to detect genetic differences among individuals. Genotyping these markers across a sample of the population allows scientists to quantify genetic variation by identifying allele frequencies and heterozygosity levels.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers
Population Sampling and Statistical Measures
To estimate genetic variation accurately, representative sampling of individuals from the population is essential. Statistical measures like allele frequency, heterozygosity, and nucleotide diversity are calculated from the data to quantify variation. These metrics provide insights into the genetic structure and evolutionary potential of the population.
Recommended video:
Guided course
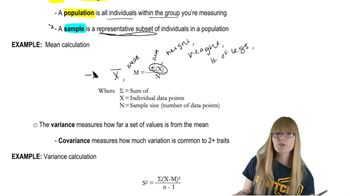
Mathematical Measurements
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
383
views


