What is the difference between a transition mutation and a transversion mutation?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
Types of Mutations
Problem C.4a
Textbook Question
Explain the following processes involving chromosome mutations and cancer development.
How the chromosome mutation producing the Philadelphia chromosome leads to CML.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the Philadelphia chromosome is a specific chromosomal abnormality resulting from a translocation between chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, denoted as t(9;22)(q34;q11).
Recognize that this translocation fuses part of the BCR gene from chromosome 22 with part of the ABL1 gene from chromosome 9, creating a novel fusion gene called BCR-ABL1.
Know that the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene encodes a constitutively active tyrosine kinase enzyme, which means it is always 'on' and continuously signals cells to proliferate.
Understand that this abnormal signaling leads to uncontrolled growth and division of myeloid cells in the bone marrow, disrupting normal blood cell production.
Connect this uncontrolled proliferation of myeloid cells to the development of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), a type of cancer characterized by excessive accumulation of these abnormal white blood cells.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Philadelphia Chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome is a specific abnormal chromosome formed by a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22. This translocation fuses the BCR gene from chromosome 22 with the ABL gene from chromosome 9, creating the BCR-ABL fusion gene, which produces an abnormal tyrosine kinase protein.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Chromosome Mutation and Translocation
Chromosome translocation is a mutation where segments from two different chromosomes swap places. This can disrupt normal gene function or create fusion genes, leading to altered cellular behavior. In the case of the Philadelphia chromosome, this mutation activates oncogenic pathways.
Recommended video:
Guided course
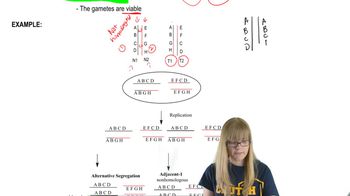
Reciprocal Translocation
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Development
CML is a type of cancer caused by the uncontrolled proliferation of white blood cells due to the BCR-ABL fusion protein's constant tyrosine kinase activity. This abnormal signaling promotes cell division and inhibits apoptosis, leading to leukemia progression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genetics of Development
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1085
views


