Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dihybrid Cross
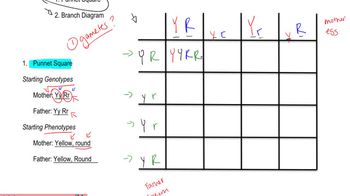
A dihybrid cross involves two traits, each represented by two alleles, allowing the study of inheritance patterns for two genes simultaneously. In this case, the genes R and T are being analyzed for their interactions in producing different phenotypes. The F₂ generation results from crossing F₁ hybrids, revealing phenotypic ratios that reflect the combinations of alleles inherited from the parents.
Recommended video:
Epistasis
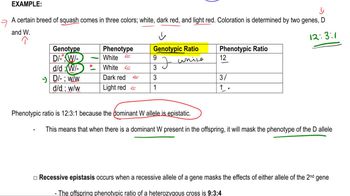
Epistasis occurs when the expression of one gene is affected by another gene, leading to modified phenotypic ratios. In the context of the question, the dominant alleles R and T may interact in such a way that they influence pigment production differently, resulting in the observed ratios of white, green, and yellow phenotypes. Understanding this interaction is crucial for designing pathways that explain the F₂ ratios.
Recommended video:
Loss-of-Function Alleles
Loss-of-function alleles are mutations that result in a gene product that is nonfunctional, often leading to a lack of a specific trait. In this scenario, the recessive alleles at both loci (r and t) are null alleles, meaning they do not contribute to pigment production. This concept is essential for understanding how the presence of dominant alleles can lead to varying phenotypes based on their functional roles in the biochemical pathway.
Recommended video: