Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nucleotides
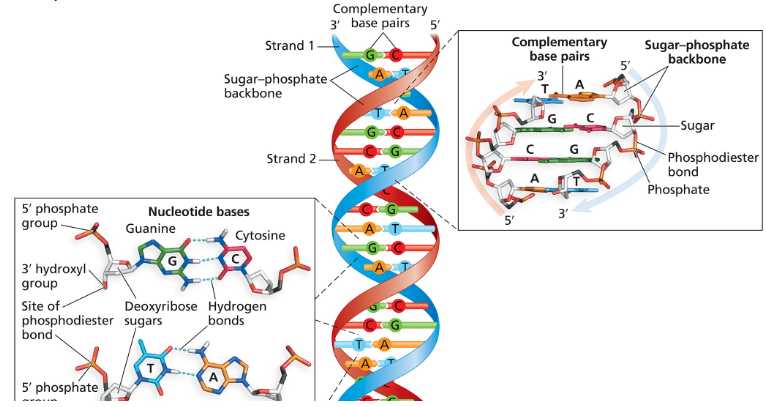
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, consisting of three components: a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine in DNA). The sequence of these nucleotides encodes genetic information, and their arrangement determines the structure and function of nucleic acids.
Recommended video:
Complementary Base Pairing
In DNA, complementary base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases across the two strands of the double helix. Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T) and guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C) through hydrogen bonds, which stabilize the DNA structure and ensure accurate replication and transcription of genetic information.
Recommended video:
Phosphodiester Bond
A phosphodiester bond is a type of covalent bond that links nucleotides together in a single strand of DNA or RNA. It forms between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another, creating a sugar-phosphate backbone that provides structural integrity to the nucleic acid molecule.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

