A hereditary disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait1. The wild-type allele of the disease gene produces a mature mRNA that is 1250 nucleotides (nt) long. Molecular analysis shows that the mature mRNA consists of four exons that measure 400 nt (exon 1), 320 nt (exon 2), 230 nt (exon 3), and 300 nt (exon 4). A mother and father with two healthy children and two children with the disease have northern blot analysis performed in a medical genetics laboratory. The results of the northern blot for each family member are shown here. Identify the genotype of each family member, using the sizes of mRNAs to indicate each allele. (For example, a person who is homozygous wild type is indicated as '1250/1250.')
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
18. Molecular Genetic Tools
Methods for Analyzing DNA
Problem 17
Textbook Question
Although the capture and trading of great apes has been banned in 112 countries since 1973, it is estimated that about 1000 chimpanzees are removed annually from Africa and smuggled into Europe, the United States, and Japan. This illegal trade is often disguised by simulating births in captivity. Until recently, genetic identity tests to uncover these illegal activities were not used because of the lack of highly polymorphic markers (markers that vary from one individual to the next) and the difficulties of obtaining chimpanzee blood samples. A study was reported in which DNA samples were extracted from freshly plucked chimpanzee hair roots and used as templates for PCR. The primers used in these studies flank highly polymorphic sites in human DNA that result from variable numbers of tandem nucleotide repeats. Several offspring and their putative parents were tested to determine whether the offspring were 'legitimate' or the product of illegal trading. The data are shown in the following Southern blot.
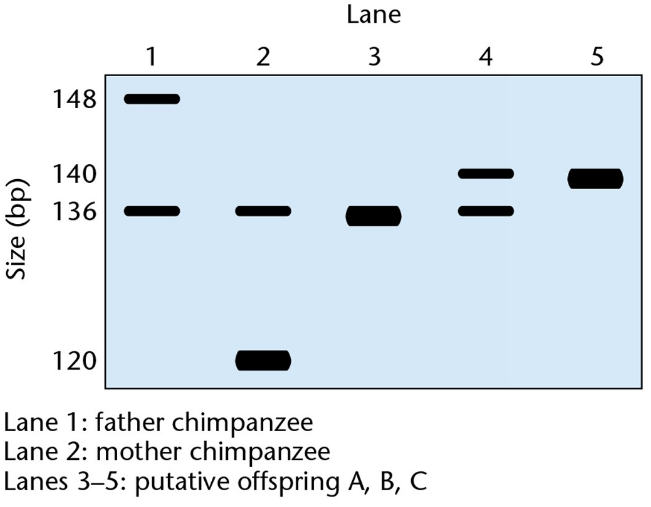
Examine the data carefully and choose the best conclusion.
a. None of the offspring is legitimate.
b. Offspring B and C are not the products of these parents and were probably purchased on the illegal market. The data are consistent with offspring A being legitimate.
c. Offspring A and B are products of the parents shown, but C is not and was therefore probably purchased on the illegal market.
d. There are not enough data to draw any conclusions. Additional polymorphic sites should be examined.
e. No conclusion can be drawn because 'human' primers were used.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: The problem involves using DNA polymorphic markers (variable number tandem repeats, VNTRs) amplified by PCR to verify parentage of chimpanzee offspring, similar to human forensic or paternity testing.
Recall the principle of inheritance for VNTR markers: Each offspring inherits one allele from each parent at a given locus, so the offspring's band pattern should be a combination of bands present in the mother and father.
Analyze the Southern blot data by comparing the band patterns of each offspring with those of the putative parents. For each offspring, check if every band can be accounted for by at least one parent’s band.
Determine legitimacy: If an offspring has bands not present in either parent, it suggests that the offspring is not genetically related to those parents and may have been illegally traded or purchased.
Evaluate the options based on your analysis of the band patterns and inheritance rules, considering whether the data are sufficient or if additional markers are needed to confirm parentage conclusively.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs)
VNTRs are DNA regions where a short nucleotide sequence is repeated a variable number of times among individuals. These highly polymorphic markers are useful for genetic fingerprinting because the number of repeats differs between individuals, allowing for identification and parentage testing.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteomics
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Specificity
PCR is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences using primers that flank the target region. Using primers designed for human VNTRs can still amplify similar regions in closely related species like chimpanzees due to genetic similarity, enabling analysis despite cross-species primer use.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genetic Cloning
Parentage Testing Using Genetic Markers
Parentage testing compares genetic markers between offspring and putative parents to verify biological relationships. Offspring inherit one allele from each parent at polymorphic loci, so mismatches at these loci can indicate non-parentage or illegal trade in animals.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers

 7:40m
7:40mWatch next
Master Methods for Analyzing DNA and RNA with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
380
views
