Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Autosomal recessive inheritance refers to a pattern where two copies of a mutated gene (one from each parent) are necessary for an individual to express a trait or disorder. In the case of alkaptonuria, individuals must inherit two copies of the mutant HAO gene to exhibit symptoms. Carriers, who possess one normal and one mutant allele, do not show symptoms but can pass the mutant allele to their offspring.
Recommended video:
Restriction Enzymes and Restriction Mapping
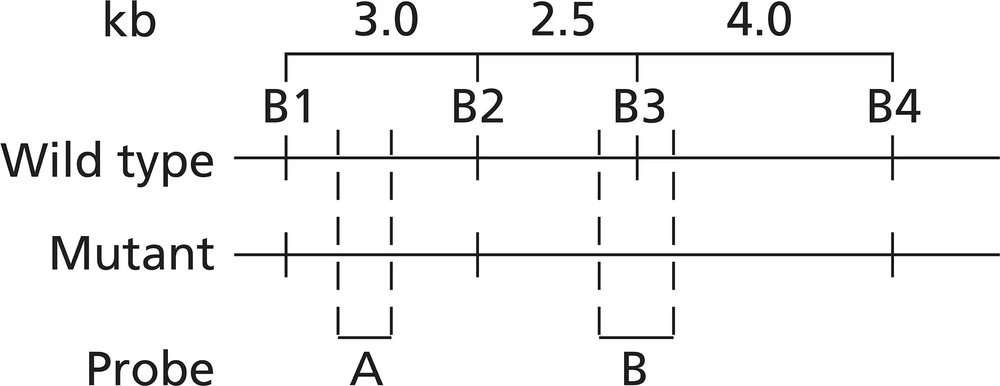
Restriction enzymes, like BamHI, cut DNA at specific sequences, allowing researchers to create restriction maps that illustrate the locations of these cut sites. In this scenario, the presence of different numbers of BamHI sites in the wild-type and mutant alleles helps identify genetic differences. Analyzing these patterns through techniques like Southern blotting can reveal the genotypes of individuals based on the presence or absence of specific bands in the gel.
Recommended video:
Missense Mutation
A missense mutation occurs when a single nucleotide change results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in a protein. In the context of alkaptonuria, the Ser-to-Thr missense mutation in the HAO gene alters the enzyme's function, leading to the accumulation of homogentisic acid. Understanding this mutation is crucial for determining the biochemical basis of the disorder and its inheritance pattern.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

