Describe the molecular composition and arrangement of the components in the nucleosome.

Contrast the various categories of repetitive DNA.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Types of Repetitive DNA

Tandem Repeats
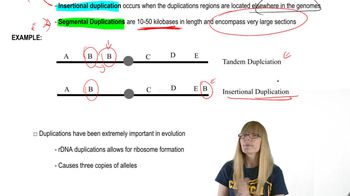
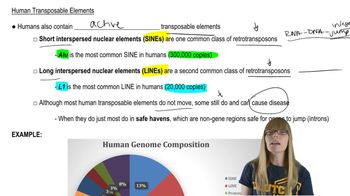
Interspersed Repeats
Describe the transitions that occur as nucleosomes are coiled and folded, ultimately forming a chromatid.
Provide a comprehensive definition of heterochromatin and list as many examples as you can.
Define satellite DNA. Describe where it is found in the genome of eukaryotes and its role as part of chromosomes.
Contrast the structure of SINE and LINE DNA sequences. Why are LINEs referred to as retrotransposons?
Mammals contain a diploid genome consisting of at least 10⁹ bp. If this amount of DNA is present as chromatin fibers, where each group of 200 bp of DNA is combined with 9 histones into a nucleosome and each group of 6 nucleosomes is combined into a solenoid, achieving a final packing ratio of 50, determine:
(a) the total number of nucleosomes in all fibers,
(b) the total number of histone molecules combined with DNA in the diploid genome, and
(c) the combined length of all fibers.
