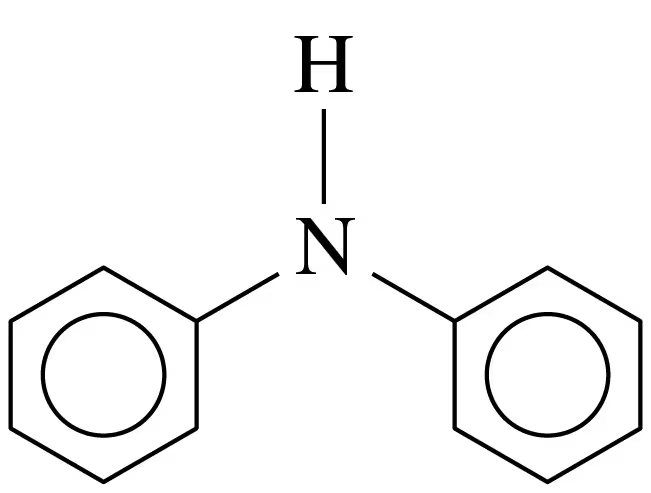
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point. Explain why you placed them in that order.
a.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:32m
1:32mMaster Acid-Base Reaction Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning