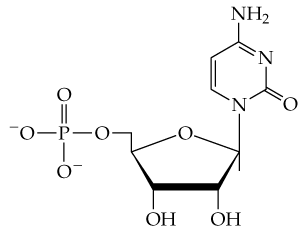
Textbook Question
Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.
962
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: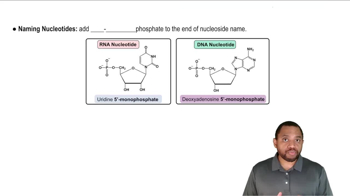
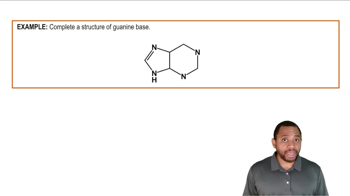
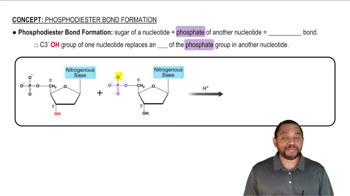

 1:41m
1:41mMaster Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning