Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions:
a. acetic acid, HC2H3O2, a weak electrolyte
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: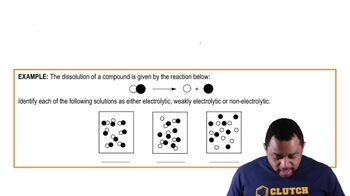

 2:38m
2:38mMaster Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning