Textbook Question
Determine whether each of the following is the cis or the trans stereoisomer:
(c)
655
views

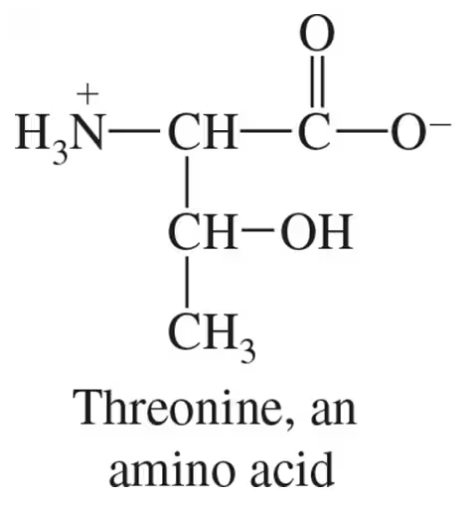
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Determine whether each of the following is the cis or the trans stereoisomer:
(c)
Determine whether each of the following is the cis or the trans stereoisomer:
(b)
Draw the skeletal structure and give the name and omega number of the following fatty acid:
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2HC=CHCH2HC=CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*).
(d)
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*).
(d)
Are the following compounds structural isomers, cis–trans isomers, or enantiomers?
(c)