Answer the following questions for the elements from cerium through lutetium:
a. Are they metals or nonmetals?
b. To what general class of elements do they belong?
c. What subshell is being filled by electrons in these elements?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
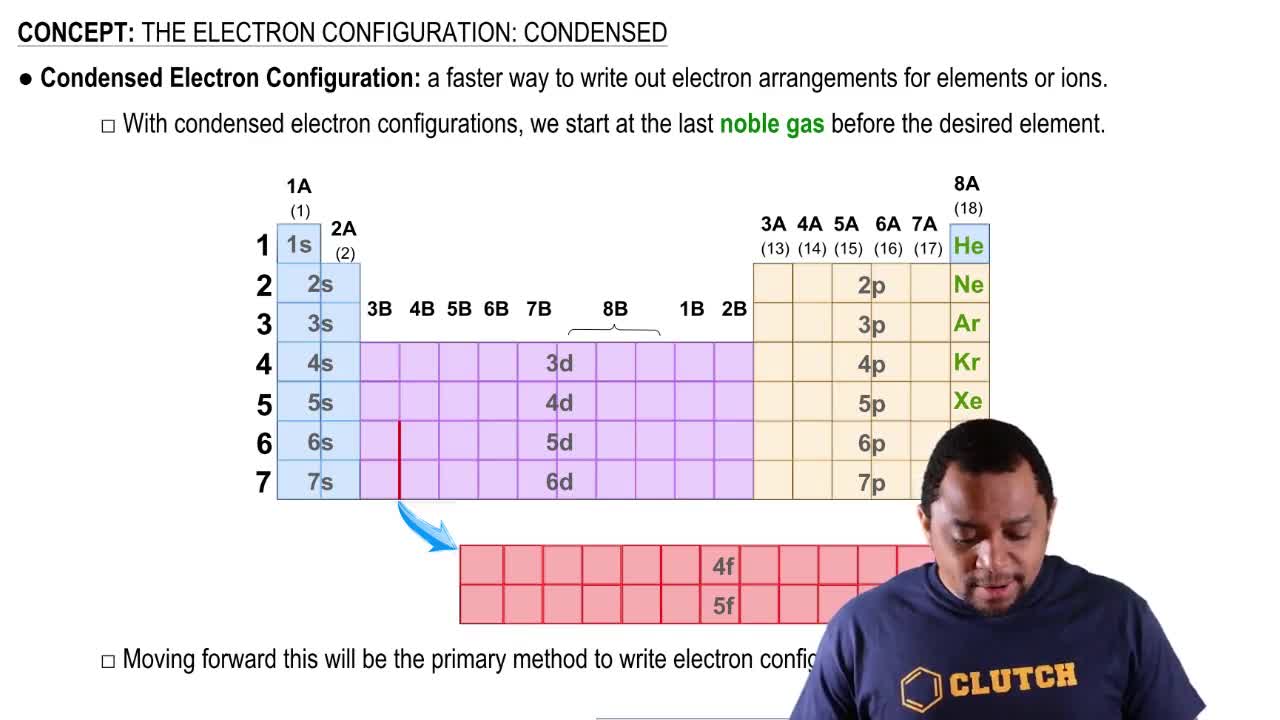
Answer the following questions for the elements from cerium through lutetium:
a. Are they metals or nonmetals?
b. To what general class of elements do they belong?
c. What subshell is being filled by electrons in these elements?
What is the total number of orbitals in the third shell? The fourth shell?
How many subshells are there in the third shell? The fourth shell? The fifth shell?
What is the mass (in amu and in grams) of a single atom of Carbon-12?
What is the mass (in grams) of 6.02 × 1023 atoms of Carbon-12?
An unidentified element is found to have an electron configuration by shell of 2 8 18 8 2. To what group and period does this element belong? Is the element a metal or a nonmetal? How many protons does an atom of the element have? What is the name of the element? Write its electron-dot symbol.