What type of interaction would you expect between the following in a tertiary structure?
a. threonine and glutamine

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



What type of interaction would you expect between the following in a tertiary structure?
a. threonine and glutamine
Draw the condensed structural formula for Ser–Lys–Asp.
Would you expect to find this segment at the center or at the surface of a protein? Why?
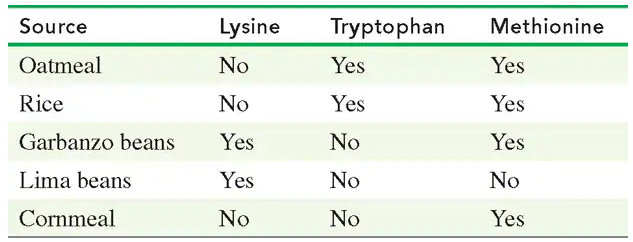
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
a. rice and lima beans
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
c. oatmeal and lima beans
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
c. polar and nonpolar amino acids