Identify the components (1 to 6) contained in each of the following lipids (a to d):
1. glycerol
2. fatty acid
3. phosphate
4. amino alcohol
5. steroid nucleus
6. sphingosine
d. triacylglycerol

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
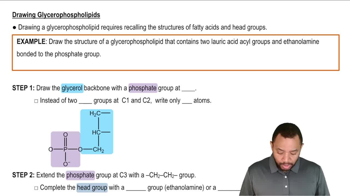

Identify the components (1 to 6) contained in each of the following lipids (a to d):
1. glycerol
2. fatty acid
3. phosphate
4. amino alcohol
5. steroid nucleus
6. sphingosine
d. triacylglycerol
Which of the following are found in cell membranes?
a. cholesterol
b. triacylglycerols
c. carbohydrates
Which of the following are found in cell membranes?
a. proteins
b. waxes
c. phospholipids
Sunflower seed oil can be used to make margarine. A triacylglycerol in sunflower seed oil contains two linoleic acids and one oleic acid.
b. Using one of the isomers, write the reaction that takes place when sunflower seed oil is used to make solid margarine.
Match the lipoprotein (1 to 4) with its description (a to d).
1. chylomicrons
2. VLDL
3. LDL
4. HDL
b. transports most of the cholesterol to the cells
Match the lipoprotein (1 to 4) with its description (a to d).
1. chylomicrons
2. VLDL
3. LDL
4. HDL
b. “bad” cholesterol