Textbook Question
Classify each of the following pure substances as an element or a compound:
b. hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
1733
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


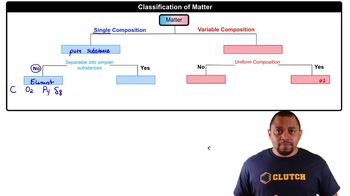
Classify each of the following pure substances as an element or a compound:
b. hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Classify each of the following pure substances as an element or a compound:
d. rust (Fe2O3)
Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture:
c. ice (H2O)
Indicate whether each of the following describes a gas, a liquid, or a solid:
a. Lemonade has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container
Indicate whether each of the following describes a gas, a liquid, or a solid:
b. The particles in a tank of oxygen are very far apart.
Indicate whether each of the following describes a gas, a liquid, or a solid:
c. Helium occupies the entire volume of a balloon.