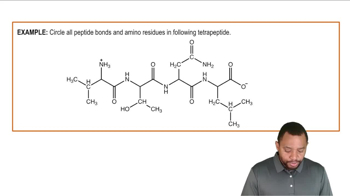
Tripeptides are composed of three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Given a set of amino acids, you can make several different tripeptides.
a. Use the three-letter shorthand notations to name all the tripeptides that can be made from serine, tyrosine, and glycine. Each amino acid will be used once in each tripeptide.