Fresh pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins.
<IMAGE>
b. Fresh pineapple is used in a marinade to tenderize tough meat. Why?
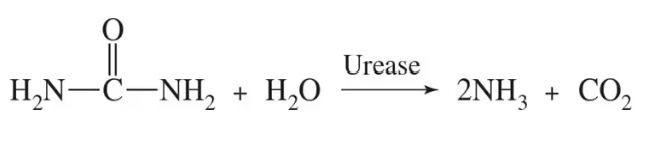
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:6m
1:6mMaster Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning