Textbook Question
FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
a. When a molecule is dehydrogenated, is FAD oxidized or reduced?
1419
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
a. When a molecule is dehydrogenated, is FAD oxidized or reduced?
FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
b. Is FAD an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent?
FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
d. What is the form of FAD after dehydrogenation?
Where in the cell does the citric acid cycle take place?
What is the final fate of the carbons in acetyl-CoA after several turns of the citric acid cycle?
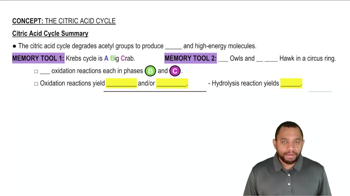
Look at the eight steps of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and answer the following questions:
a. Which steps involve oxidation reactions?