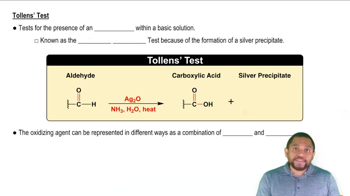
Identify each of the following changes of state as melting, freezing, sublimation, or deposition:
a. Dry ice in an ice-cream cart disappears.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Identify each of the following changes of state as melting, freezing, sublimation, or deposition:
a. Dry ice in an ice-cream cart disappears.
Identify each of the following changes of state as melting, freezing, sublimation, or deposition:
b. Snow on the ground turns to liquid water.
Identify each of the following changes of state as melting, freezing, sublimation, or deposition:
c. Heat is removed from 125 g of liquid water at 0 °C.
Using the values for the heat of fusion, specific heat of water, and/or heat of vaporization, calculate the amount of heat energy in each of the following:
c. kilojoules needed to melt 24.0 g of ice at 0 °C, warm the liquid to 100 °C, and change it to steam at 100 °C
Using energy values from TABLE 3.8, determine each of the following:
c. If Charles consumes 1800 kcal per day, he will maintain his weight. Would he lose weight on his new diet?
Using energy values from TABLE 3.8, determine each of the following:
d. If expending 3500 kcal is equal to a loss of 1.0 lb, how many days will it take Charles to lose 5.0 lb?