In humans, the antibiotic amoxicillin (a type of penicillin) is used to treat certain bacterial infections.
c. Is amoxicillin a reversible or irreversible inhibitor?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


In humans, the antibiotic amoxicillin (a type of penicillin) is used to treat certain bacterial infections.
c. Is amoxicillin a reversible or irreversible inhibitor?
Ethylene glycol (HO—CH2—CH2—OH) is a major component of antifreeze. If ingested, it is first converted to HOOC—CHO (oxoethanoic acid) and then to HOOC—COOH (oxalic acid), which is toxic.
<IMAGE>
a. What class of enzyme catalyzes the reactions described?
Ethylene glycol (HO—CH2—CH2—OH) is a major component of antifreeze. If ingested, it is first converted to HOOC—CHO (oxoethanoic acid) and then to HOOC—COOH (oxalic acid), which is toxic.
<IMAGE>
b. The treatment for the ingestion of ethylene glycol is an intravenous solution of ethanol. How might this help prevent toxic levels of oxalic acid in the body?
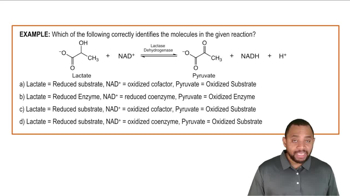
Adults who are lactose intolerant cannot break down the disaccharide in milk products. To help digest dairy food, a product known as Lactaid can be given prior to consuming dairy products. (16.4, 16.5)
b. What might happen to the enzyme if the Lactaid were stored at 55 °C?
Fresh pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins.
<IMAGE>
a. The directions for a gelatin (protein) dessert say not to add fresh pineapple. However, canned pineapple where pineapple is heated to high temperatures can be added. Why?
Fresh pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins.
<IMAGE>
b. Fresh pineapple is used in a marinade to tenderize tough meat. Why?