How and where does sucrose undergo digestion in the body? Name the products.

Which of the following reactions in glycolysis produce ATP or NADH?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Glycolysis

ATP Production
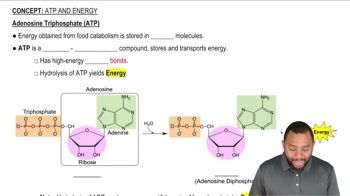
NADH Production

If glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and the citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, how do the products of glycolysis get inside the mitochondrial matrix?
Which of the following reactions in glycolysis produce ATP or NADH?
a. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate
Which of the reactions given in Problems 12.72 represent isomerizations where the reactants and products are structural isomers?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
b. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
c. dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 12.11 to answer each of the following:
d. Name the reactions where secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones.
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 12.11 to answer each of the following:
c. Name the reaction that is coupled to GTP formation.
