Which of the following terms apply to the compound shown below? (Hint: Look at the functional groups and the bonds involved to begin analyzing the compound part by part in comparison to the lipids discussed in this chapter.)
a. A phospholipid
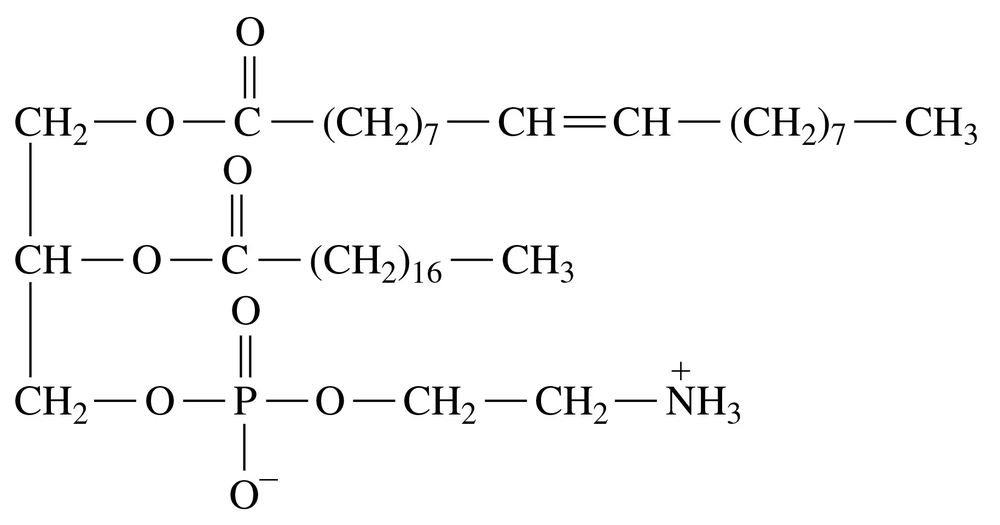
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 2:5m
2:5mMaster Glycerophospholipids Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning