Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following amides with NaOH:
d.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following amides with NaOH:
d.
Draw the condensed structural formulas and write the IUPAC names for two structural isomers of the carboxylic acids that have the molecular formula C4H8O2.
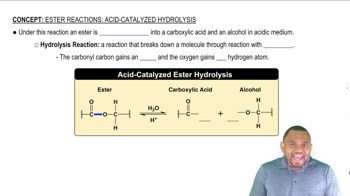
The ester methyl butanoate has the odor and flavor of strawberries.
a. Draw the condensed structural formula for methyl butanoate.
<IMAGE>
Methyl benzoate, which smells like pineapple guava, is used to train detection dogs.
b. Write the IUPAC name for the carboxylic acid and alcohol used to prepare methyl benzoate.
<IMAGE>
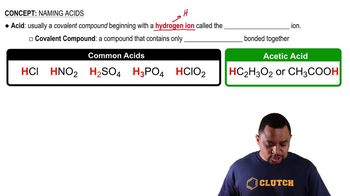
There are four amine isomers with the molecular formula C3H9N. Draw their condensed structural formulas, write the common name, and classify each as a primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) amine.
There are four amide isomers with the molecular formula C3H7NO. Draw their condensed structural formulas and write the IUPAC name for each.