Textbook Question
What disulfides would you obtain from oxidation of the following thiols?
a. CH3CH2CH2SH
b. 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol (skunk scent)
802
views

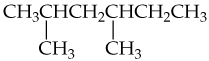
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What disulfides would you obtain from oxidation of the following thiols?
a. CH3CH2CH2SH
b. 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol (skunk scent)
Give systematic names for the following alkyl halides:
a.
b.
2-Aminopropane is an achiral molecule, but 2-aminobutane is chiral. Explain.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
The compound pictured here is a thiol. (a) Draw its line structure, and (b) draw the structure of the disulfide formed when it is treated with an oxidizing agent (yellow = S).
<IMAGE>
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
a. 2,4-Dimethyl-2-heptanol