Match each of the following physical and chemical properties with ethane, C2H6 or sodium bromide, NaBr:
b. burns vigorously in air
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: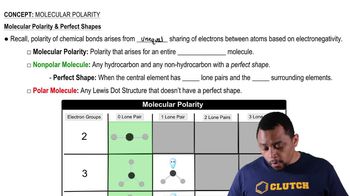



 2:26m
2:26mMaster Introduction to Organic Chemistry Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning