Match the following physical and chemical properties with potassium chloride, KCl, used in salt substitutes, or butane, C4H10 used in lighters:
<IMAGE>
e. is a gas at room temperature

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Problem 44b
Problem 44b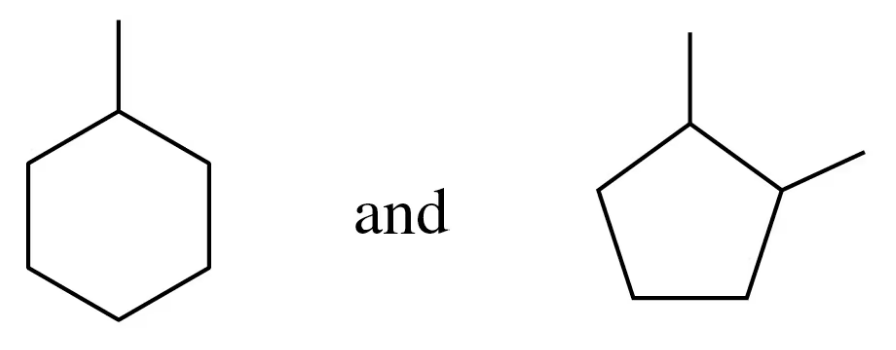
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Match the following physical and chemical properties with potassium chloride, KCl, used in salt substitutes, or butane, C4H10 used in lighters:
<IMAGE>
e. is a gas at room temperature
Match the following physical and chemical properties with octane, C8H18 found in gasoline, or magnesium sulfate, MgSO4 also called Epsom salts:
a. contains only covalent bonds
Match the following physical and chemical properties with octane, C8H18 found in gasoline, or magnesium sulfate, MgSO4 also called Epsom salts:
d. is a liquid at room temperature
Convert each of the following line-angle formulas to a condensed structural formula and give its IUPAC name:
a.
Convert each of the following line-angle formulas to a condensed structural formula and give its IUPAC name:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
c.