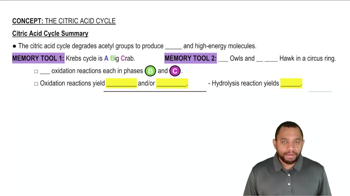
Look at the eight steps of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and answer the following questions:
a. Which steps involve oxidation reactions?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 :50m
:50mMaster Phase A - Citrate Formation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning