Caprylic acid, CH3 ― (CH2)6 ― COOH, is a C8 fatty acid found in milk.
a. State the number of β oxidation cycles for the complete oxidation of caprylic acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

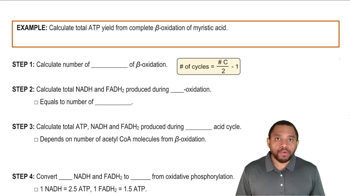

 3:8m
3:8mMaster Total Energy from Fatty Acids Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning