How many equivalents of an acid or base are in the following?
a. 0.25 mol Mg(OH)2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

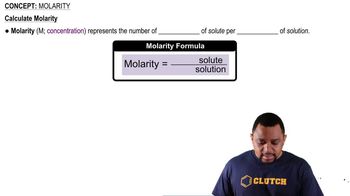

How many equivalents of an acid or base are in the following?
a. 0.25 mol Mg(OH)2
What are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 5.0 g of Ca(OH)2 in enough water to make 500.0 mL of solution?
What are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 25 g of citric acid (triprotic, C6H5O7H3) in enough water to make 800 mL of solution?
The dissociation of water into H3O+ and OH– ions depends on temperature. At 0 °C the [H3O+] = 3.38 x 10–8 M, at 25 °C the [H3O+] = 1.00 x 10–7 M, and at 50 °C the [H3O+] = 2.34 x 10–7 M.
b. What is the value of Kw at 0 °C and 50 °C?
The dissociation of water into H3O+ and OH– ions depends on temperature. At 0 °C the [H3O+] = 3.38 x 10–8 M, at 25 °C the [H3O+] = 1.00 x 10–7 M, and at 50 °C the [H3O+] = 2.34 x 10–7 M.
c. Is the dissociation of water endothermic or exothermic?
One of the buffer systems used to control the pH of blood involves the equilibrium between H2PO4– and H2PO42–. The pKa for H2PO42– is 7.21.
a. Write the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for this buffer system.