Identify the amino acids and type of interaction that occurs between the following R groups in tertiary protein structures:
c. —CH2—SH and HS—CH2—
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: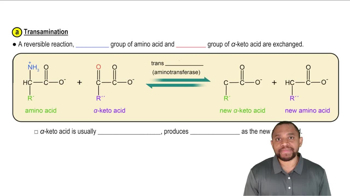



 2:7m
2:7mMaster Tertiary Protein Structure Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning