Textbook Question
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of the oxidation of D-galactose at C1.
750
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
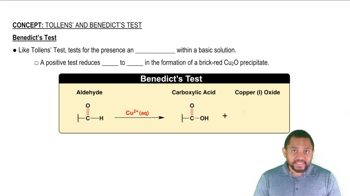


Draw the Fischer projection of the product of the oxidation of D-galactose at C1.
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of reduction reaction of D-galactose at C1.
Will the following carbohydrates produce a positive Benedict's test?
a. D-glucose
Draw the product of the following 1→4 condensation and name the glycosidic bond:
Isomaltose, a disaccharide formed during caramelization in cooking, contains two glucose units bonded ⍺(1→6). Draw the structure of isomaltose.
The glycosidic bond in a disaccharide was determined to be α(1→6). Hydrolysis of the disaccharide produced one galactose and one fructose. Draw the structure of the disaccharide.