From what alcohols might the following carbonyl-containing products have been made (red = O, reddish-brown = Br)?
(a) <IMAGE>
(b) <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: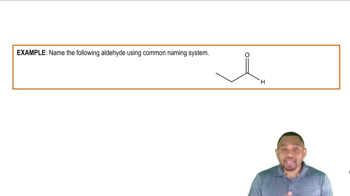



 1:49m
1:49mMaster Alcohol Reactions: Oxidation Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning