How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers? Identify each as the D- or L-isomer.
(a)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

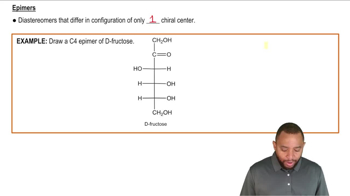
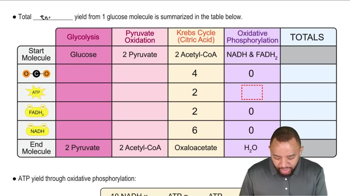
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers? Identify each as the D- or L-isomer.
(a)
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers? Identify each as the D- or L-isomer.
(b)
How are the following pairs of carbohydrates, shown in a Fischer projection, related to each other? Are they structural isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or epimers?
(a)
Identify the following carbohydrates as the ⍺ or β anomer:
(a)
Identify the following carbohydrates as the ⍺ or β anomer:
(b)
Draw the Fischer projection of the product of the oxidation of D-galactose at C1.