Textbook Question
Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(d)
578
views

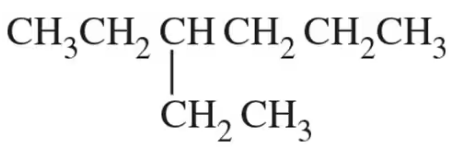
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Mark the chiral centers in the following molecules, if any, with an asterisk (*):
(d)
Convert each of the Lewis structures shown into a condensed structural formula:
(c)
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(a)
Convert the condensed structures shown to skeletal structures.
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(a)
Convert the skeletal structures shown to condensed structures.
(b)