Which weighs more, 5.00 g or 0.0225 mol of acetaminophen (C8H9O2)?

The reaction of ethylene oxide with water to give ethylene glycol (automobile antifreeze) occurs in 96.0% actual yield. How many grams of ethylene glycol are formed by reaction of 35.0 g of ethylene oxide? (For ethylene oxide, MW = 44.0 amu; for ethylene glycol, MW = 62.0 amu.)
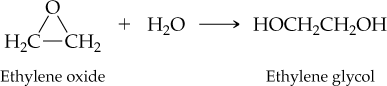
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Stoichiometry

Molar Mass

Percent Yield

Balance the following equation, and tell how many moles of nickel will react with 9.81 mol of hydrochloric acid.
Ni(s) + HCl(aq) → NiCl2(aq) + H2(g)
How many moles of NiCl2 can be formed in the reaction of 6.00 mol of Ni and 12.0 mol of HCl?
Ni(s) + HCl(aq) → NiCl2(aq) + H2(g)
The following diagram represents the reaction of A2(red spheres) with B2(blue spheres):
<IMAGE>
b. How many moles of product can be made from 1.0 mol of A2? From 1.0 mol of B2?
Consider the balanced chemical equation: 2A + B2 → 2AB. Given the following reaction vessel, determine the theoretical yield of product.
<IMAGE>
Consider the balanced chemical equation: A2 + 2 B2 → 2 AB2. A reaction is performed with the initial amounts of A2 and B2 shown in part (a). The amount of product obtained is shown in part (b). Calculate the percent yield.
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
