Textbook Question
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
a. XCl3
1101
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
a. XCl3
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
b. Al2X3
Identify the group number in the periodic table of X, a representative element, in each of the following ionic compounds:
b. X2SO3
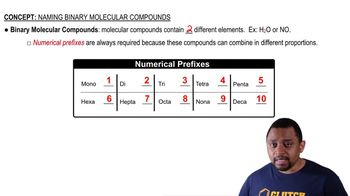
Classify each of the following as ionic or molecular, and name each:
b. Cl2O7
Complete the Lewis structure for each of the following:
a.
Identify the errors in each of the following Lewis structures and draw the correct formula:
c.