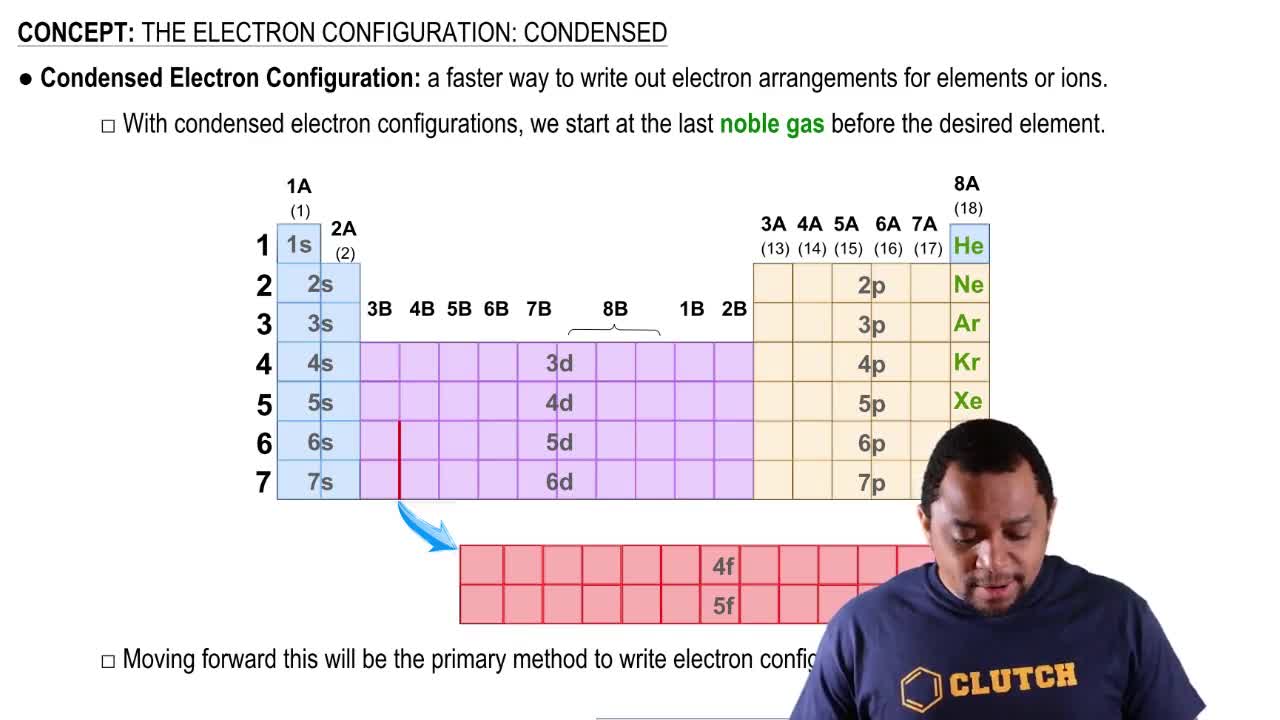
Textbook Question
One of these pictures represents a solution of HCl and one represents a solution of H2SO4. Which is which?
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
1529
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


One of these pictures represents a solution of HCl and one represents a solution of H2SO4. Which is which?
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
The elements in red in the periodic table can form cations having more than one charge. Write the formulas and names of the compounds that are formed between the red cations and the blue anions depicted in the periodic table.
Which of the following ions are likely to form? Explain.
a. Li2+
b. K-
c. Mn3+
d. Zn4+
e. Ne+
Write equations for the loss of an electron by a K atom and the gain of an electron by a K+ ion.
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Write equations to show how the substances listed in Problem 3.75 give ions when dissolved in water.
a. H2CO3
b. HCN
c. Mg(OH)2
d. KOH