Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
c. Organic solvents

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
c. Organic solvents
Fresh pineapple cannot be used in gelatin desserts because it contains an enzyme that hydrolyzes the proteins in gelatin, destroying the gelling action. Canned pineapple can be added to gelatin with no problem. Why?
As a chef, you prepare a wide variety of foods daily. The following dishes all contain protein. What method (if any) has been used to denature the protein present in each food?
a. Charcoal-grilled steak
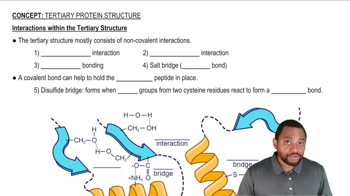
Oxytocin is a small peptide that is used to induce labor by causing contractions in uterine walls. It has the primary structure Cys-Tyr-Ile-Gln-Asn-Cys-Pro-Leu-Gln. This peptide is held in a cyclic configuration by a disulfide bridge. Draw a diagram of oxytocin, showing the disulfide bridge.
Four of the most abundant amino acids in proteins are leucine, alanine, glycine, and valine. What do these amino acids have in common? Would you expect these amino acids to be found on the interior or on the exterior of the protein?
Globular proteins are water-soluble, whereas fibrous proteins are insoluble in water. Indicate whether you expect the following amino acids to be on the surface of a globular protein or on the surface of a fibrous protein.
a. Ala