Write the base sequence in a complementary DNA segment if each original segment has the following base sequence:
d. A T A T G C G C T A A A
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

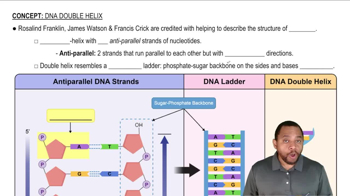

 2:56m
2:56mMaster Base Pairing Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning