Identify the solute and the solvent in each solution composed of the following:
a. 10.0 g of NaCl and 100.0 g of H2O

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
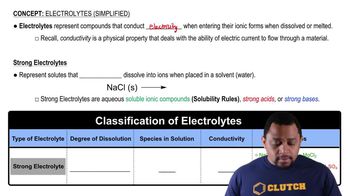

Identify the solute and the solvent in each solution composed of the following:
a. 10.0 g of NaCl and 100.0 g of H2O
Describe the formation of an aqueous KI solution, when solid KI dissolves in water.
Water is a polar solvent and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a nonpolar solvent. In which solvent is each of the following, which is found or used in the body, more likely to be soluble?
d. cholesterol (lipid), nonpolar
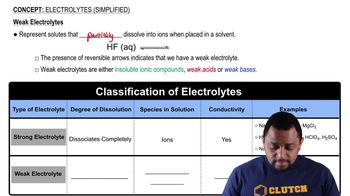
Write a balanced equation for the dissociation of each of the following strong electrolytes in water:
d. Fe(NO3)3
Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions:
a. acetic acid, HC2H3O2, a weak electrolyte
Indicate whether aqueous solutions of each of the following solutes contain only ions, only molecules, or mostly molecules and a few ions:
b. NaBr, a strong electrolyte