Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
a. Which lipoprotein has the lowest density? Why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: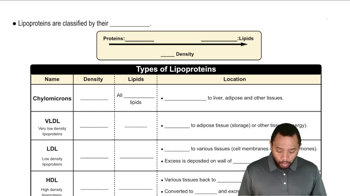



 1:39m
1:39mMaster Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning