Textbook Question
How does the polarity of the R group in leucine compare to the R group in serine?
1443
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

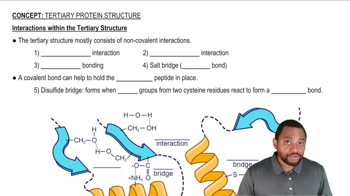

How does the polarity of the R group in leucine compare to the R group in serine?
Draw the structure for each of the following amino acids at physiological pH:
a. lysine
Classify each of the amino acids in problem 16.5 as polar or nonpolar. If polar, indicate if the R group is neutral, acidic, or basic. Indicate if each is hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Write the name for the amino acid represented by each of the following abbreviations:
d. G
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following peptides, and give its three-letter and one-letter abbreviations:
a. alanylcysteine
Draw the condensed structural formula for each of the following peptides, and give its three-letter and one-letter abbreviations:
c. glycylalanylvaline