Balance each of the following chemical equations:
c. Sb2S3(s) + HCl(aq) → SbCl3(aq) + H2S(g)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: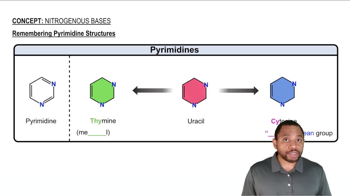

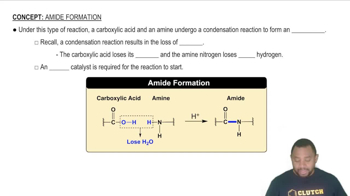

 1:32m
1:32mMaster Balancing Chemical Equations (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning